数据类型
值类型/原始类型/非引用类型
- number
- bigint
- string
- boolean
- symbol
- null
- undefined
bigint 1
- 用于解决大数计算的问题
- 只能是整数
- 不能使用 Math 的内置方法计算
- 不能 number 混合计算
- 不能 new
- 转换为数字时可能导致精度丢失
- 字面量为数值+n:
1n,1111n - 0n !== 0 0n == 0
symbol 2
- 一种特殊的字符串,用作唯一标识
- 常被用来给对象增加属性防止属性冲突
- 用作属性值无法被枚举(Object.keys, for in, Object.getOwnPropertyNames)
- 不能 new
- 用作属性可使用 Object.getOwnPropertySymbols 进行获取
number
- 存在数值溢出问题、计算精度问题。
- 计算精度可使用整数转换来解决
- 数值溢出可使用 bigint 解决
进制转换:(number).toString(进制)
IEEE 754 双精度浮点数。
全局 Symbol
- Symbol.for(string) 可以在全局的 Symbol 中注册一个全局 Symbol,该 Symbol 在再次调用 Symbol.for(string) 时会返回。
- Symbol.keyFor(symbol) 可以获取全局 Symbol 的 key。
通用 Symbol
- Symbol.hasInstance - 自定义 instanceof 行为
- Symbol.iterator - 自定义迭代器行为,for-of 调用
- Symbol.asyncIterator - 自定义 async 迭代器行为,for-await-of 调用
- Symbol.toPrimitive - 自定义对象的原始类型转换行为
- Symbol.toStringTag - 自定义对象的 toString 行为,Object.prototype.toString 调用
引用类型/复杂类型
新手要注意多变量指向同一个引用,当引用中的属性变更时会影响所有变量。
function
new 5
new 执行以下几步操作:
- 首先创建一个空对象
- 设置空对象的原型,如果构造函数的 prototype 为对象则设置为它,否则维持不变
- 执行构造函数,并将创建对象作为 this 上下文
- 构造函数执行完成后如果返回了一个非原始值,将会使用该值作为创建的实例,否则使用创建的对象作为返回值
原型链 4
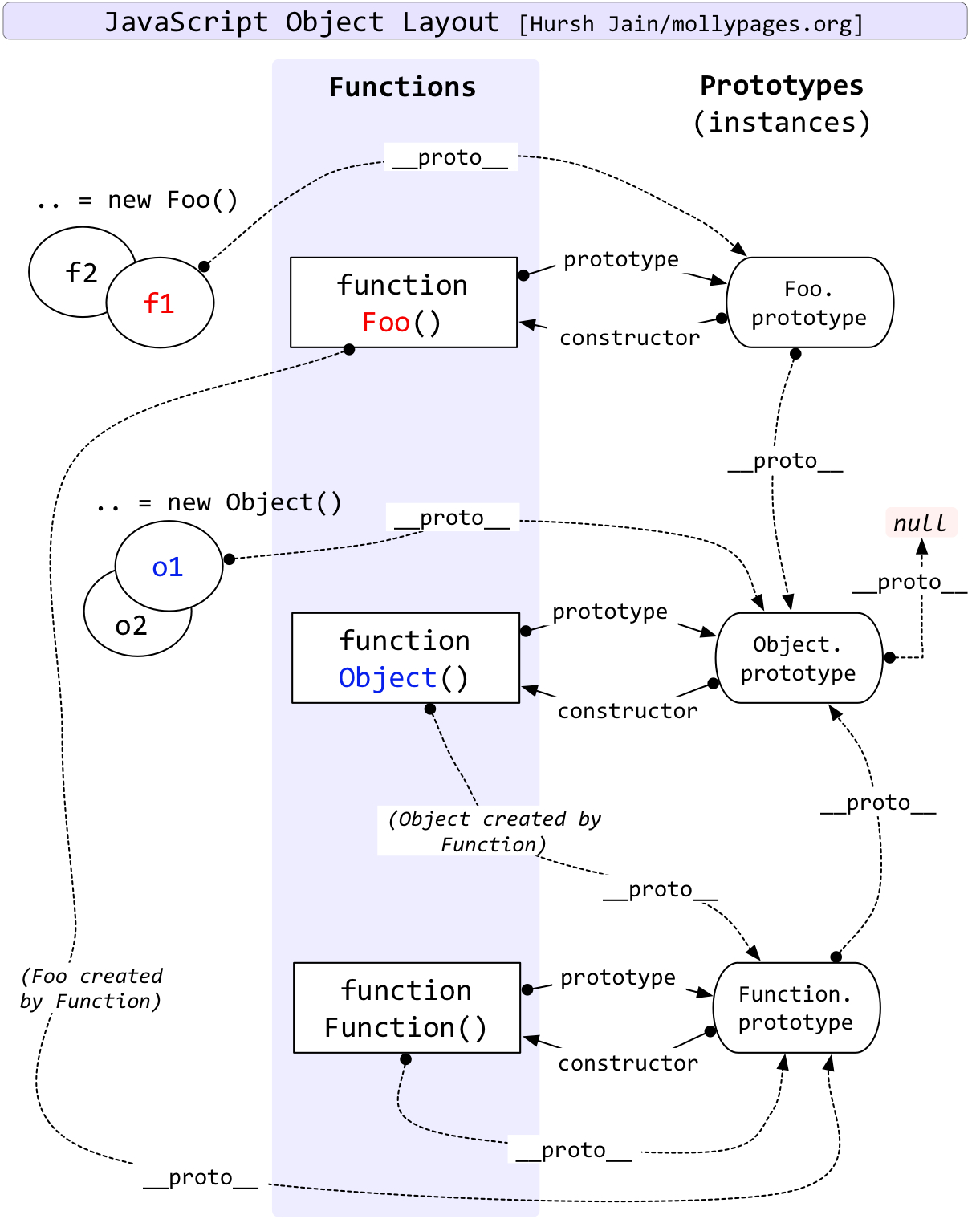
JS 原型继承的特点:
继承属性不可删改,可读,修改时会在自身创建
继承属性可以被 for in 迭代,需要使用 hasOwnProperty 判断(顶层 Object 原型上的属性基本均为 enumerable false,不可枚举,所以不会被 for in 所枚举)
原型继承呈现链状,所以称为原型链
几乎所有对象原型链的顶端都为 Object 函数的 prototype,除了 Object.create(null);
对象字面量的原型为 Object 函数的 prototype
Object.prototype 的原型为 null
可以通过 Object.getPrototypeOf 获取对象/包装对象的原型
Object.constructor 为 Function
Function.prototype 的 prototype 为 Object.prototype
Object.prototype.constructor 为 Object
Function.constructor 为 Function => Function instanceof Function
Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.getPrototypeOf(Object)).constructor 为 Object => Object instance Object
Function instanceof Object, Object instanceof Function
Object.create(null).toString();
// error
包装类型
所有基础类型的属性访问都通过包装类型来实现。
'aaa'.length;
const s = 'string';
s.length = 4;
s._a = 1;
类型转换
隐式类型转换
显式类型转换
堆存储和栈存储
隐式类型循环引用导致的内存泄露
值传递和引用传递
类型判断
instanceof
一般用于判断是否为对应类型的实例,本质是检查右值 prototype 是否在左值的原型鲢上。基本类型的
- Object instanceof Object
- Function instanceof Function
- Object instanceof Function
- Function instanceof Object
通过 Symbol.hasInstance 自定义 instanceof 行为:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Symbol/hasInstance
es 标准定义:https://tc39.es/ecma262/multipage/ecmascript-language-expressions.html#sec-instanceofoperator > https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23622695/why-in-javascript-both-object-instanceof-function-and-function-instanceof-obj
typeof
| 类型 | typeof 返回值 |
|---|---|
| null | object |
| undefined | undefined |
| boolean | boolean |
| number | number |
| bigint | bigint |
| string | string |
| symbol | symbol |
| function | function |
| class | function |
| object | object |
| array | object |
| 其它 | object |
typeof null === 'Object' 的原因:
在早期的 JS 中,JS 中的值使用类型标识+值来表示,object 的类型标识为 0,typeof 使用类型标识来判断类型。 而 null 使用空指针实现,大部分环境下空指针指向
0x00,导致 null 的类型标识为 0,而后期由于存量的页面导致无法变更。所以只是一个无法修复的历史 bug。
参考链接:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/typeof#typeof_null
其它
使用 Object toString 获取类型
function getType(v: any) {
return {}.toString.call(v).replace('[object ', '').replace(']', '');
}
! 注意遇到基本类型的对象实例会翻车:
getType(new String(''));
// String
Array.isArray 判断数组
Number.isNaN 判断 NaN
常规方案
- 通过 === null 和 === undefined 判断出两个特殊类型
- 通过 typeof 判断出其它基本类型
- 通过 Object toString 判断出复杂类型
Typeof
const allTypesOfValue = [null, undefined, true, 1, NaN, Infinity, 'string', Symbol('symbol'), () => {}, {}, [], /1/, new Date()];
const tableTypeof = [];
allTypesOfValue.forEach(v => {
tableTypeof.push({
value: v,
typeofResult: typeof v
});
});
console.table(tableTypeof);
| value | TypeofResult |
|---|---|
| null | object |
| undefined | undefined |
| true | boolean |
| 1 | number |
| NaN | number |
| Infinity | number |
| 'string' | string |
| Symbol('symbol') | symbol |
| () => {} | function |
| {} | object |
| [] | object |
| /1/ | object |
| new Date() | object |
It's a bug of typeof null is equal to object, but this is unable to change
if a variable is an Object, type of it will return object or function, and it's not equal to null, so:
function isObject(v) {
const type = typeof v;
return v !== null && (type === 'function' || type === 'object');
}
Object.prototype.toString
In MDN Object.prototype.toString
toString()can be used with every object and allows you to get its class.
const allTypesOfValue = [null, undefined, true, 1, NaN, Infinity, 'string', Symbol('symbol'), () => {}, {}, [], /1/, new Date()];
const tableToString = [];
allTypesOfValue.forEach(v => {
tableToString.push({
value: v,
toStringResult: Object.prototype.toString.call(v)
});
});
console.table(tableToString);
| value | toStringResult |
|---|---|
| null | [object Null] |
| undefined | [object Undefined] |
| true | [object Boolean] |
| 1 | [object Number] |
| NaN | [object Number] |
| Infinity | [object Number] |
| 'string' | [object String] |
| Symbol('symbol') | [object Symbol] |
| () => {} | [object Function] |
| {} | [object Object] |
| [] | [object Array] |
| /1/ | [object RegExp] |
| new Date() | [object Date] |
How to know type of a variable
Use toString to get variable's type
Object.prototype.toString can be used to get variable's type
In Underscore
_.each(['Arguments', 'Function', 'String', 'Number', 'Date', 'RegExp', 'Error'], function (name) {
_['is' + name] = function (obj) {
return toString.call(obj) === '[object ' + name + ']';
};
});
Instanceof
From MDN:
The instanceof operator tests whether the
prototypeproperty of a constructor appears anywhere in the prototype chain of an object.
function A() {
this.a = 1;
}
const a = new A();
a instanceof A; // true
Some thing interesting:
Object instanceof Object; // true
Object instanceof Function; // true
Function instanceof Object; // true
Function instanceof Function; // true
instanceof operator will check is there some __proto__ from the right is inherit from the left's prototype.
From ibm-developer
function instance_of(L, R) {
//L 表示左表达式,R 表示右表达式
var O = R.prototype; // 取 R 的显示原型
L = L.__proto__; // 取 L 的隐式原型
while (true) {
if (L === null) return false;
if (O === L)
// 这里重点:当 O 严格等于 L 时,返回 true
return true;
L = L.__proto__;
}
}
data type conversion
Comparison operators
Abstract Equality Comparison(==)
There is some strangely comparison, such as:
null == undefined; // true
(NaN ==
NaN + // false
0) ==
-0; // true
1 == '1'; // true same as 1 === Number('1')
1 == true; // true same as 1 === Number(true) Number(true) is equal to 1 and Number(false) is equal to 0
2 == true; // false
'[object Object]' == { a: 1 }; // true same as "[object Object]" === ({a:1}).toString()
123 == new Number(123); // true same as 123 === (new Number(123)).valueOf()
'Wed Feb 07 2018 10:44:41 GMT+0800 (CST)' == new Date(); // true same as "Wed Feb 07 2018 10:44:41 GMT+0800 (CST)" == (new Date).toString()
It's because of the rules in the ecma
The comparison x == y, where x and y are values, produces true or false. Such a comparison is performed as follows:
- If Type(x) is the same as Type(y), then
- If Type(x) is Undefined, return true.
- If Type(x) is Null, return true.
- If Type(x) is Number, then
- If x is NaN, return false.
- If y is NaN, return false.
- If x is the same Number value as y, return true.
- If x is +0 and y is −0, return true.
- If x is −0 and y is +0, return true.
- Return false.
- If Type(x) is String, then return true if x and y are exactly the same sequence of characters (same length and same characters in corresponding positions). Otherwise, return false.
- If Type(x) is Boolean, return true if x and y are both true or both false. Otherwise, return false.
- Return true if x and y refer to the same object. Otherwise, return false.
- If x is null and y is undefined, return true.
- If x is undefined and y is null, return true.
- If Type(x) is Number and Type(y) is String, return the result of the comparison x == ToNumber(y).
- If Type(x) is String and Type(y) is Number, return the result of the comparison ToNumber(x) == y.
- If Type(x) is Boolean, return the result of the comparison ToNumber(x) == y.
- If Type(y) is Boolean, return the result of the comparison x == ToNumber(y).
- If Type(x) is either String or Number and Type(y) is Object, return the result of the comparison x == ToPrimitive(y).
- If Type(x) is Object and Type(y) is either String or Number, return the result of the comparison ToPrimitive(x) == y.
- Return false.
| Operand B | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undefined | Null | Number | String | Boolean | Object | ||
| Operand A | Undefined | true | true | false | false | false | false |
| Null | true | true | false | false | false | false | |
| Number | false | false | A === B | A === ToNumber(B) | A === ToNumber(B) | A == ToPrimitive(B) | |
| String | false | false | ToNumber(A) === B | A === B | ToNumber(A) === ToNumber(B) | A == ToPrimitive(B) | |
| Boolean | false | false | ToNumber(A) === B | ToNumber(A) === ToNumber(B) | A === B | ToNumber(A) == ToPrimitive(B) | |
| Object | false | false | ToPrimitive(A) == B | ToPrimitive(A) == B | ToPrimitive(A) == ToNumber(B) | A === B |
ToPrimitive
var a = {};
a.toString = () => {
console.log('toString');
return {};
};
a.valueOf = () => {
console.log('valueOf');
return {};
};
a == '';
/**
valueOf
toString
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive value
*/
When compare Object to String or Number, js will call the toPrimitive of the Object without hint, toPrimitive will call valueOf and
toString in order then no hint, when one of them return primitive value, will return the camparison of the primitive value, or throw a exception
like the code above.
Strict Equality Comparison(===)
-0 === +0; // true
In ecma
- If Type(x) is different from Type(y), return false.
- If Type(x) is Undefined, return true.
- If Type(x) is Null, return true.
- If Type(x) is Number, then
- If x is NaN, return false.
- If y is NaN, return false.
- If x is the same Number value as y, return true.
- If x is +0 and y is −0, return true.
- If x is −0 and y is +0, return true.
- Return false.
- If Type(x) is String, then return true if x and y are exactly the same sequence of characters (same length and same characters in corresponding positions); otherwise, return false.
- If Type(x) is Boolean, return true if x and y are both true or both false; otherwise, return false.
- Return true if x and y refer to the same object. Otherwise, return false.
Object.is
Object.is is like ===,besides of number compare:
Object.is(+0, -1); // false
Object.is(NaN, NaN); // true
| x | y | == | === | Object.is | SameValueZero |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
undefined | undefined | true | true | true | true |
null | null | true | true | true | true |
true | true | true | true | true | true |
false | false | true | true | true | true |
'foo' | 'foo' | true | true | true | true |
0 | 0 | true | true | true | true |
+0 | -0 | true | true | false | true |
+0 | 0 | true | true | true | true |
-0 | 0 | true | true | false | true |
0 | false | true | false | false | false |
"" | false | true | false | false | false |
"" | 0 | true | false | false | false |
'0' | 0 | true | false | false | false |
'17' | 17 | true | false | false | false |
[1, 2] | '1,2' | true | false | false | false |
new String('foo') | 'foo' | true | false | false | false |
null | undefined | true | false | false | false |
null | false | false | false | false | false |
undefined | false | false | false | false | false |
{ foo: 'bar' } | { foo: 'bar' } | false | false | false | false |
new String('foo') | new String('foo') | false | false | false | false |
0 | null | false | false | false | false |
0 | NaN | false | false | false | false |
'foo' | NaN | false | false | false | false |
NaN | NaN | false | false | true | true |